Hebei ZhenXing JinYuan Wire Mesh Group offers a Stainless Steel Expanded Metal Mesh Sheet, made from premium SS 304 and 316 materials. Known for its durability and resilience, our stainless steel mesh ensures a robust and lasting solution. Committed to meeting customer expectations in quality, durability, and performance, our expanded metal sheets typically feature a standard rhombic (diamond) shape, combining aesthetic appeal with functionality. This mesh pattern is visually attractive and offers excellent strength and rigidity, suitable for diverse applications. Available as flattened panels, our sheets provide a smooth surface, facilitating easy installation and versatility in both industrial and decorative settings.
General specifications of Stainless Steel Expanded Metal Mesh Sheet
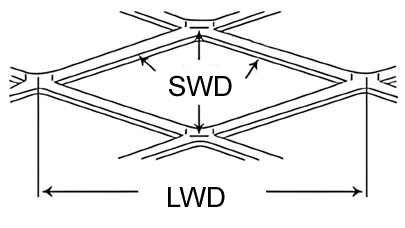
- LWD (Long Way of Diamond)
Description: The length of the long diagonal of the diamond.
Common Values: 12.7 mm to 76.2 mm. - SWD (Short Way of Diamond)
Description: The length of the short diagonal of the diamond.
Common Values: 5.8 mm to 38.1 mm. - Thickness
Description: The depth of the sheet material.
Common Values: 0.5 mm to 8 mm. - Strand Width
Description: Width of the individual strands or ribs of metal.
Common Values: 1.2 mm to 8 mm. - SWM (Short Way of Mesh)
Description: Distance from the middle of one bond to the middle of the next along the short axis.
Common Values: 5.8 mm to 38.1 mm. - LWM (Long Way of Mesh)
Description: Distance from the middle of one bond to the middle of the next along the long axis.
Common Values: 12.7 mm to 76.2 mm. - Bond
Description: The intersection where strands are bonded together.
Common Characteristics: Provides stability and rigidity to the mesh.
These values are typical ranges for Stainless Steel Expanded Metal Mesh Sheets. Specific dimensions can vary depending on the application.
Material
The material used for Stainless Steel Expanded Metal Mesh Sheets is typically SS 304 and SS 316. Both SS 304 and SS 316 provide the Expanded Metal Mesh Sheets with strength, longevity, and resistance to various environmental factors, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial to architectural.
- SS 304: This is the most commonly used stainless steel. It’s an austenitic steel known for its corrosion resistance, durability, and weldability. SS 304 is suitable for a wide range of applications and environments, especially where resistance to rust and corrosion is essential.
- SS 316: This stainless steel is similar to SS 304 but with the addition of molybdenum, which significantly enhances its corrosion resistance, particularly against chlorides and other industrial solvents. SS 316 is often used in more demanding environments, such as marine applications or in chemical processing industries.
Mesh Shaped Pattern
The mesh shape in expanded metal sheets can vary, but the most common designs are:
- Diamond-shaped mesh: The most typical pattern for expanded metal, where the sheet has been cut and stretched to form small diamond-shaped openings. This pattern provides a combination of strength and open area.
- Hexagonal mesh: Similar to diamond mesh but with six-sided openings, giving it a honeycomb appearance. This type is less common but offers unique aesthetic and functional characteristics.
- Square or Rectangular mesh: In these designs, the openings are square or rectangular. They offer a more uniform and grid-like appearance and are often used for specific industrial applications.
- Heavy Type (Tortoise-shaped): Stronger, more rigid design with a unique pattern.
- Decorative patterns: Some expanded metal sheets are made with intricate, decorative patterns. These are less about function and more about aesthetic appeal, often used in architectural or design contexts.
These shapes are created through a process where a stainless steel sheet is simultaneously slit and stretched, creating openings in the material. The choice of shape depends on the intended use, with factors like strength, airflow, and aesthetic playing a role in the selection.
Overall Appearance
Expanded metal mesh made from stainless steel can typically be found in two overall forms:
- Flat Sheets: This is the most common form, where the expanded metal is processed into flat panels. These sheets are often used for architectural purposes, fencing, walkways, and various industrial applications. The flatness allows for easy installation and provides a consistent surface area .
- Rolls: Expanded metal can also be supplied in roll form, especially for lighter gauges. Rolls are more convenient for applications requiring longer lengths of material without joins or seams. They are often used in applications like filters, screens, and various industrial uses where the material might need to be cut or shaped to specific requirements.
- Raised Panels: Raised panels in expanded metal mesh are a type of fabrication that gives the mesh a three-dimensional profile instead of a flat one. Achieved during manufacturing, this method results in a raised mesh pattern where the metal is slit, stretched, but not flattened. The strands and bonds angle away from the sheet’s plane, creating a raised surface. This textured surface enhances grip and anti-skid properties, making it ideal for applications requiring slip resistance, like walkways and steps. These panels blend functionality and aesthetics , providing strength, safety, and visual appeal for various uses.
The choice between flat sheets and rolls depends on the application’s specific needs, including the scale of the project, the ease of installation, and the type of application. Flat sheets are preferable for more structural or precise applications, while rolls are more suited for covering larger areas or for applications where the material will be further processed or customized.
Surface Treatment
The most common surface treatment for Stainless Steel Expanded Metal Mesh, particularly for grades like SS 304 and SS 316, focuses on enhancing its natural corrosion resistance and improving its aesthetic appeal. The primary treatment used is:
- Passivation: This is the most typical surface treatment for stainless steel mesh. Passivation involves treating the steel with a mild acid solution, usually citric or nitric acid, to remove any free iron from the surface. This process helps in enhancing the natural chromium oxide layer, which provides stainless steel with its corrosion-resistant properties. The passivation process does not significantly change the appearance of the steel but ensures its surface is fully passive and resistant to corrosion, especially in environments where it may come into contact with corrosive agents.
Classification by Application
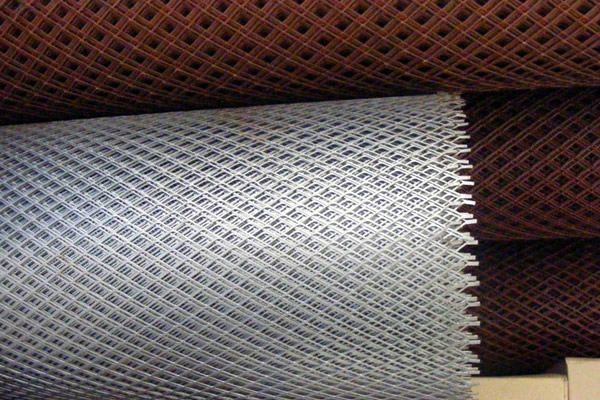
Material: Typically SS 304 or SS 316 for corrosion resistance.
Process: Cut and stretched into a diamond pattern, often polished for aesthetic enhancement.
Use: Used in facades, cladding, and interior designs for aesthetic appeal and functionality.
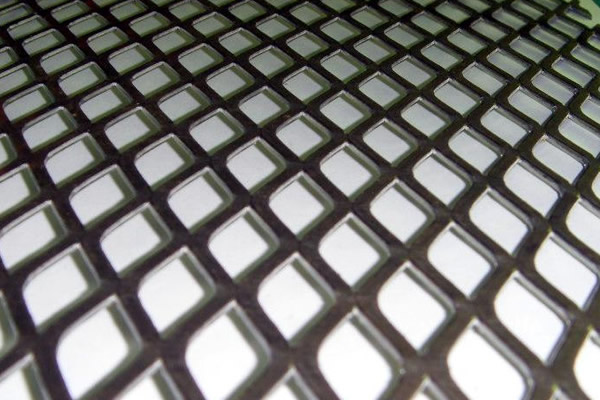
Material: Mainly SS 316 for enhanced corrosion resistance in industrial settings.
Process: Emphasis on strength during cutting and stretching, often passivated for extra durability.
Use: Ideal for platforms, walkways, and barriers in industrial environments.
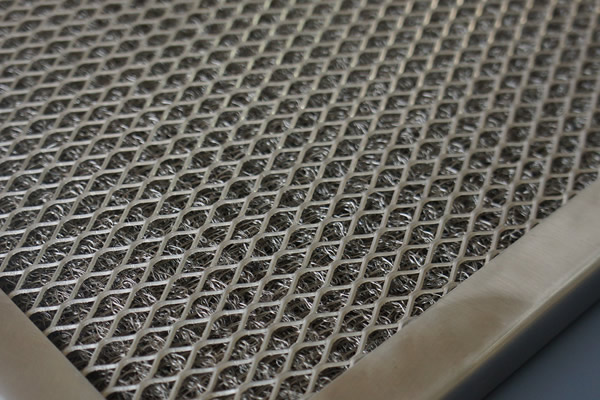
Material: SS 304 is common for its cost-effectiveness and corrosion resistance.
Process: Precision manufacturing for specific pore sizes and shapes.
Use: Applied in filtration systems across various industries for liquid and gas purification.
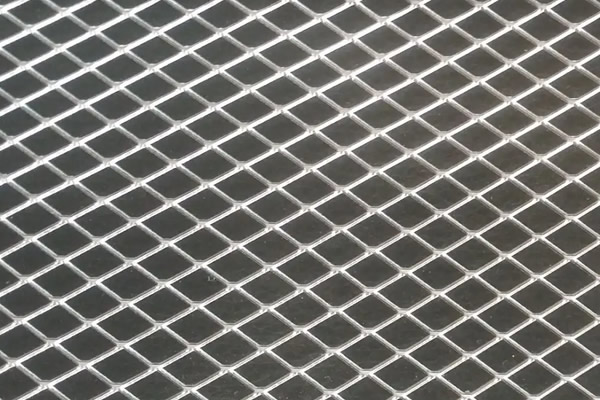
Material: SS 304 used for its weather resistance and durability.
Process: Cut and stretched into desired patterns, sometimes coated for weather protection.
Use: Utilized in outdoor furniture, fencing, and landscaping elements.