The production process of steel grating involves several critical steps to ensure the final product is durable, reliable, and meets the necessary specifications. Here’s a detailed overview of each step in the process:
Material
The initial phase in steel grating production involves selecting the appropriate steel type, like low-carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, tailored to the intended use and environmental conditions. Options encompass Smooth Flat Steel Bar for regular gratings, Serrated Bar for anti-slip surfaces in moist areas, and I Bar for lightweight yet strong applications focusing on weight reduction. Subsequently, a quality check ensures the steel meets essential standards in composition and strength.
Welding
Welding plays a vital role in steel grating production and varies according to the bar type: Smooth Flat, Serrated (Toothed), or I Bar. Smooth Flat Steel Bars typically undergo resistance welding, where pressure and current are applied for a uniform, strong bond. Serrated Bars, with their uneven surface, require precise alignment during resistance welding, demanding adjustments in the welding head and pressure, followed by thorough joint inspection. For I Bars, distinct in shape, either resistance welding or specialized methods are used, focusing on proper alignment of the flanges with cross rods and addressing challenges in heat distribution and pressure for a robust weld.
- Weld Integrity: It’s crucial for welds to be robust and consistent across all bar types to maintain the grating’s structural integrity.
- Controlled Environment: The welding area must be kept free of contaminants that could compromise weld strength.
- Expertise Required: Competent welders are critical, particularly for complex bar types like serrated or I Bars.
- Inspection and Testing: After welding, the grating is subject to thorough inspections and potential tests (such as load tests) to verify that the welding adheres to necessary standards.
Cutting
- Smooth Flat Steel Bar: Cut using oxy-fuel, plasma cutting, or shearing. plasma cutting is preferred for precision and clean edges.
- Serrated (Toothed) Bar: Requires careful cutting due to irregular surface; plasma cutting is often used for precision. important to maintain the consistency and functionality of serrations.
- I Bar: Unique shape demands precision cutting techniques like laser cutting or precision saw cutting. focus on preserving structural integrity and avoiding warping.
- General Cutting Considerations: Ensure dimensional accuracy and smooth edges.minimize material waste and maintain equipment for clean cuts.Handle materials properly and ensure safety during cutting.
End Plate Welding
End plates are added as per the design requirements, considering the type of bar used to ensure proper alignment and structural integrity.
Hot Dipped Galvanizing
The chosen type of steel bar is subjected to galvanizing for corrosion resistance. The process remains largely the same, although care is taken to account for the different shapes and textures, especially in the case of serrated bars.
Packaging
After the galvanizing process, the gratings are packaged carefully. The packaging method might vary depending on the type of bar and the size of the gratings.
Transportation
Finally, the packaged steel gratings are transported to their destination. The transportation method is chosen based on the size and quantity of the gratings, as well as the distance to the delivery location.

Material
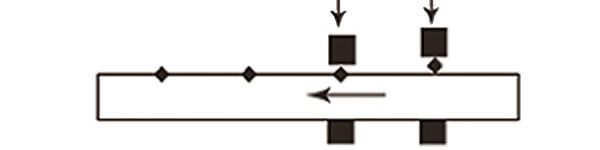
Welding
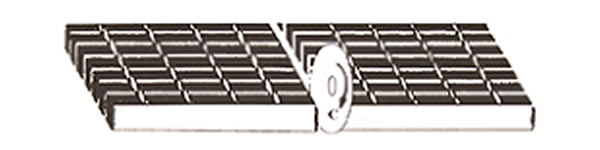
Cutting
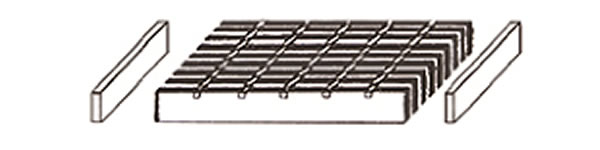
End Plate Welding
Hot Galvanizing

Final Shipment